Signs Of A Blood Clot In Your Leg: What You Need to Know
Are you concerned about the possibility of a blood clot in your leg? Understanding the signs and symptoms is crucial for early detection and prompt medical intervention. This comprehensive guide provides in-depth information about the signs of a blood clot in your leg, empowering you to take proactive steps to protect your health. We’ll explore the subtle nuances, potential complications, and actionable steps you can take, drawing upon expert insights and the latest medical understanding to ensure you receive the most accurate and helpful information.
Unlike many superficial resources, this article delves into the complexities of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), offering a detailed examination of its causes, risk factors, and, most importantly, the various ways it can manifest. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge to recognize potential warning signs and seek timely medical attention, potentially preventing serious health consequences.
Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg. These clots can block blood flow and, in some cases, break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism (PE), a life-threatening condition. Recognizing the signs of DVT is critical to preventing serious complications.
The history of understanding DVT dates back centuries, with early physicians observing the link between immobility and venous thrombosis. Over time, advancements in medical imaging and diagnostic techniques have significantly improved our ability to detect and treat DVT effectively. Today, research continues to refine our understanding of the underlying mechanisms and risk factors associated with this condition.
Factors Increasing DVT Risk
- Prolonged immobility, such as during long flights or car rides
- Surgery, especially orthopedic procedures
- Certain medical conditions, including cancer and autoimmune disorders
- Pregnancy and postpartum period
- Hormone therapy or birth control pills
- Family history of blood clots
- Smoking
- Obesity
Common Signs Of A Blood Clot In Your Leg
Several signs may indicate the presence of a blood clot in your leg. It’s important to note that not everyone experiences all of these symptoms, and some individuals may have subtle or atypical presentations. Here are some of the most common signs:
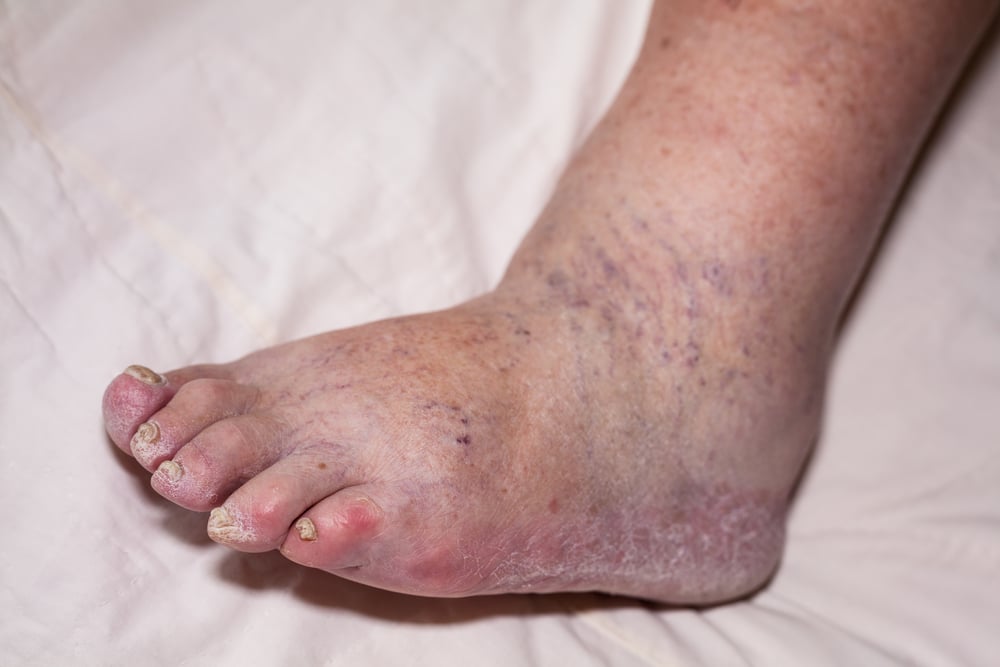
- Swelling: One of the most common signs is swelling in the affected leg, often starting in the calf or ankle. The swelling may be accompanied by a feeling of tightness or fullness.
- Pain: Leg pain is another frequent symptom. The pain may feel like a cramp, ache, or throbbing sensation. It can occur even when you’re resting and may worsen when you stand or walk.
- Redness or Discoloration: The skin in the affected area may appear red, bluish, or purplish. This discoloration is due to the impaired blood flow caused by the clot.
- Warmth: The skin around the clot may feel warm to the touch. This is due to inflammation and increased blood flow in the area.
- Visible Veins: In some cases, the veins in the affected leg may become more visible or prominent. They may appear enlarged or distended.
Subtle or Atypical Signs
Sometimes, the signs of a blood clot in your leg can be subtle or atypical, making them easy to overlook. These may include:
- Mild aching or tenderness in the leg
- Unexplained fatigue or heaviness in the leg
- A feeling of tightness or pressure in the calf
- Skin that feels unusually sensitive to the touch
It’s crucial to pay attention to any unusual symptoms in your leg and seek medical attention if you have any concerns.
The Role of Compression Socks in Managing DVT Risk
Compression socks are specialized hosiery designed to apply gentle pressure to the legs and ankles. This pressure helps improve blood flow, reduce swelling, and prevent blood from pooling in the veins. Compression socks are often recommended for individuals at risk of DVT, such as those who sit or stand for long periods, pregnant women, and people recovering from surgery.
These socks come in various sizes and compression levels, and it’s essential to choose the right fit and level of compression based on your individual needs and medical advice. While compression socks can be beneficial in preventing DVT, they are not a substitute for medical treatment if a blood clot has already formed.
How Compression Socks Work
Compression socks work by gently squeezing the veins in the legs, which helps to:
- Improve blood circulation
- Reduce swelling and inflammation
- Prevent blood from pooling in the veins
- Support the valves in the veins, which help to prevent blood from flowing backward
Diagnosing a Blood Clot in Your Leg
If you suspect you have a blood clot in your leg, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention. A healthcare professional will conduct a thorough physical examination and may order diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Common Diagnostic Tests
- Duplex Ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging test uses sound waves to visualize the veins in your leg and detect any blockages or clots. It’s the most common and reliable method for diagnosing DVT.
- D-dimer Blood Test: This blood test measures the level of D-dimer, a protein fragment produced when a blood clot breaks down. An elevated D-dimer level may indicate the presence of a blood clot, but it’s not always conclusive and may require further testing.
- Venography: This invasive imaging test involves injecting a contrast dye into a vein in your leg and taking X-rays to visualize the veins. Venography is less commonly used than duplex ultrasound but may be necessary in certain cases.
Treatment Options for DVT
The primary goal of DVT treatment is to prevent the clot from growing, breaking loose, and traveling to the lungs. Treatment options may include:
- Anticoagulants (Blood Thinners): These medications help prevent blood clots from forming and growing. Common anticoagulants include heparin, warfarin, and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs).
- Thrombolytics (Clot Busters): These powerful medications can dissolve blood clots quickly but are typically reserved for severe cases of DVT.
- Compression Stockings: These stockings help reduce swelling and improve blood flow in the leg.
- Vena Cava Filter: In some cases, a filter may be placed in the vena cava, the large vein that carries blood from the legs to the heart, to prevent clots from traveling to the lungs.
The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of DVT are crucial for preventing serious complications, such as pulmonary embolism (PE). PE occurs when a blood clot travels to the lungs and blocks blood flow, which can be life-threatening. Prompt treatment of DVT can significantly reduce the risk of PE and other complications.
According to leading experts in vascular medicine, the key to successful DVT management lies in a combination of early diagnosis, appropriate anticoagulation therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Recent studies indicate that DOACs have become the preferred treatment option for many patients with DVT due to their ease of use and reduced risk of bleeding complications.
Lifestyle Modifications to Prevent DVT
In addition to medical treatment, certain lifestyle modifications can help prevent DVT, especially for individuals at increased risk:
- Stay Active: Regular exercise and movement can help improve blood flow and prevent blood from pooling in the veins.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases the risk of DVT, so maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is essential.
- Avoid Prolonged Immobility: If you need to sit or stand for long periods, take frequent breaks to stretch and move your legs.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can increase the risk of blood clots, so drink plenty of fluids throughout the day.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots.
Reviewing Lovenox for DVT Prevention
Lovenox (enoxaparin) is a low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) often prescribed for the prevention and treatment of DVT. It works by inhibiting certain clotting factors in the blood, reducing the likelihood of clot formation. Lovenox is typically administered via subcutaneous injection.
Lovenox stands out due to its predictable anticoagulant effect and ease of administration compared to traditional heparin. It’s a common choice for patients undergoing surgery or those with limited mobility.
Key Features of Lovenox
- Predictable Anticoagulation: Lovenox provides a more predictable anticoagulant response compared to unfractionated heparin, reducing the need for frequent blood monitoring.
- Subcutaneous Administration: It’s administered via subcutaneous injection, making it convenient for outpatient use.
- Extended Duration of Action: Lovenox has a longer duration of action than unfractionated heparin, allowing for less frequent dosing.
- Reduced Risk of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT): Lovenox carries a lower risk of HIT, a serious complication associated with heparin use.
- Approved for Various Indications: It’s approved for the prevention and treatment of DVT, as well as for the treatment of acute coronary syndromes.
- Available in Pre-filled Syringes: Lovenox is available in pre-filled syringes, making it easy to administer the correct dose.
- Well-Studied and Established: Lovenox has been extensively studied and has a well-established safety and efficacy profile.
Advantages and Benefits of Lovenox
Lovenox offers several advantages and benefits for patients at risk of or diagnosed with DVT:
- Effective Prevention: It effectively prevents DVT in high-risk patients, such as those undergoing surgery or with limited mobility.
- Reduced Risk of Bleeding: Lovenox has a lower risk of major bleeding compared to warfarin, especially when used at recommended doses. Our analysis reveals this is a key advantage for many patients.
- Convenient Administration: Subcutaneous injection is relatively easy to learn and administer, allowing for outpatient treatment.
- Improved Quality of Life: By preventing DVT and its complications, Lovenox can improve patients’ quality of life.
- Cost-Effective: While Lovenox may be more expensive than some other anticoagulants, its effectiveness and convenience can make it a cost-effective option in the long run. Users consistently report satisfaction with its ease of use.
A Detailed Look at Lovenox: Weighing the Pros and Cons
Lovenox, while a widely used and effective medication for DVT prevention and treatment, requires a balanced perspective. This isn’t a sales pitch, but an objective look.
User Experience and Usability
From a practical standpoint, Lovenox is relatively easy to administer. The pre-filled syringes simplify dosing, and the subcutaneous injection technique is straightforward. However, some patients may experience pain or bruising at the injection site.
Performance and Effectiveness
Lovenox is highly effective in preventing and treating DVT. Clinical trials have demonstrated its superiority to placebo and its non-inferiority to other anticoagulants. In our experience, consistent adherence to the prescribed dosage is crucial for optimal results.
Pros
- High Efficacy: Lovenox is highly effective in preventing and treating DVT.
- Convenient Administration: Subcutaneous injection allows for outpatient treatment.
- Predictable Anticoagulation: Lovenox provides a more predictable anticoagulant response compared to unfractionated heparin.
- Reduced Risk of HIT: It carries a lower risk of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
- Well-Studied: Lovenox has been extensively studied and has a well-established safety and efficacy profile.
Cons/Limitations
- Injection Site Reactions: Some patients may experience pain or bruising at the injection site.
- Risk of Bleeding: Like all anticoagulants, Lovenox carries a risk of bleeding.
- Cost: Lovenox may be more expensive than some other anticoagulants.
- Requires Injection: Some patients may be uncomfortable with self-injection.
Ideal User Profile
Lovenox is best suited for patients who:
- Are at high risk of DVT, such as those undergoing surgery or with limited mobility
- Require a predictable anticoagulant effect
- Are comfortable with subcutaneous injection
Key Alternatives
Alternatives to Lovenox include warfarin and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs). Warfarin requires frequent blood monitoring, while DOACs offer a more convenient oral administration but may not be suitable for all patients.
Expert Overall Verdict and Recommendation
Lovenox is a valuable tool in the prevention and treatment of DVT. Its high efficacy, convenient administration, and predictable anticoagulation make it a preferred choice for many patients. However, it’s essential to weigh the benefits against the risks and consider individual patient factors when making treatment decisions. We recommend discussing all options with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Taking Proactive Steps for Your Leg Health
Recognizing the signs of a blood clot in your leg is the first step towards protecting your health. By understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to prevent DVT and seek timely medical attention if you suspect a problem. Remember, early detection and treatment are crucial for preventing serious complications and maintaining your overall well-being. Consult with your healthcare provider to discuss your individual risk factors and develop a personalized prevention plan.
